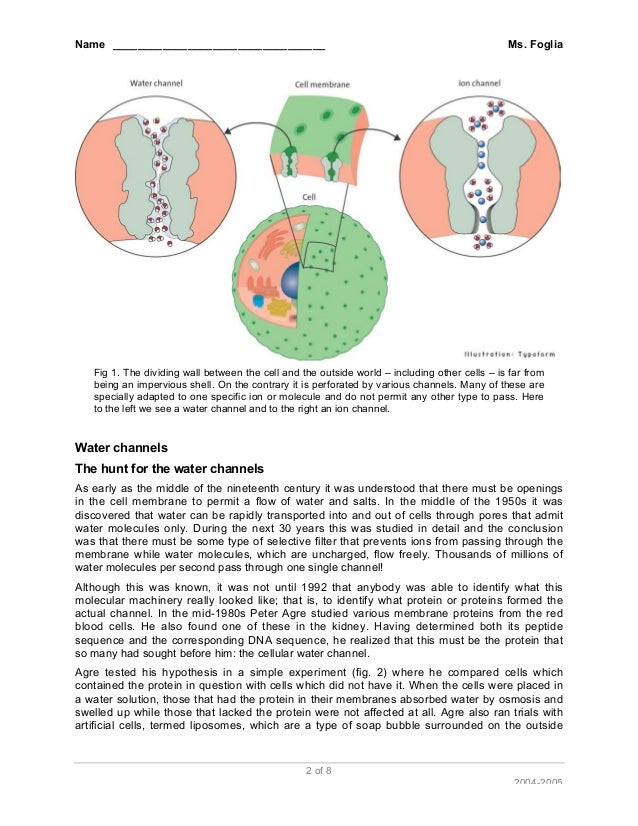
Firstly it will provide clues to the function of aquaporins at the whole plant level. In animals blood delivers the necessary.

No if you can reconstitute an aquaporin in a membrane it will function fine.
Do aquaporins require a living cell in order to function. Yes all living things are made up of cells. No if you can reconstitute an aquaporin in a membrane it will function fine. Aquaporins that actively transport water will not function but many aquaporins are passive transporters.
All the above being said we are still not close enough to use aquaporins as well as biology does. Do Aquaporins Need Living Cells to Work. Aquaporins are just water channels that allow water molecules to pass through the membrane.
They were kept in mind and work is still going on. In each system they allow water to flow across the membrane in both directions in terms of basic osmotic on both sides of the membrane. Do Aquaporins Require A.
Do aquaporins require a living cell in order to function. No if you can reconstitute an aquaporin in a membrane it will function fine. Aquaporins that actively transport water will not function but many aquaporins are passive transporters.
No aquaporins do not need a living cell in order to function. Aquaporins are water channels that permit water channels to cross membranes. Do aquaporins require a living cell in order to function.
No because its just a channel for water to pass through it doesnt need a living cell to facilitate it. It also says that Agre also ran the experiment with artificial cells and it still worked. - Aquaporins do not require a living cell in order to function because it is a mere channel for water to pass through.
How does the aquaporin prevent H ions from passing through. Functions for some aquaporins have also been suggested such as cellcell adhesion membrane polarization and regulation of interacting proteins such as ion channels. Why do some membranes need high water or glycerol permeability.
Most cells do not express aquaporins. Virtually all biological membranes are reasonably water permeable as. A different group proposes an alternative hypothesis stating that even with nonfunctional aquaporins a small amount of water will still cross the cell membrane.
An experiment is set up in which plant cells with mutated nonfunctional aquaporins and plant cells with normally functioning aquaporins are both placed in distilled water. Aquaporins also called water channels are channel proteins from a larger family of major intrinsic proteins that form pores in the membrane of biological cells mainly facilitating transport of water between cells. The cell membranes of a variety of different bacteria fungi animal and plant cells contain aquaporins through which water can flow more rapidly into and out of the cell than by diffusing.
The region of a protein that associates with a ligand known as the ligands binding site usually consists of a cavity in the protein surface formed by a particular arrangement of amino acids. These amino acids can belong to different portions of the polypeptide chain that are brought together when the protein folds Figure 3-38Separate regions of the protein surface generally provide. When an embedded protein assists in the passive transport of molecules across a barrier in the direction of the concentrated gradient from high concentration to low concentration.
The cell uses energy from ATP to move molecules across the membrane against the concentration gradient. Embedded proteins may. Aquaporins belong to the group of integral membrane proteins that are found in cell membranes.
The role of aquaporins is to allow the passage of water between cells. Aquaporins are expressed in organ- tissue- and cell type-specific manners. Knowledge of the expression patterns of different aquaporins is essential for several reasons.
Firstly it will provide clues to the function of aquaporins at the whole plant level. Water crosses cell membranes by two routes. By diffusion through the lipid bilayer and through water channels called aquaporins.
Functional characterization of the first aquaporin was reported in 1992 but water channels were suspected to exist well before that time because the osmotic permeability of some types of epithelial cells was much too large to be accounted for by simple diffusion through the. The main role of aquaporins in plants is transport of water and other small neutral molecules across cellular biological membranes. AQPs have remarkable features to provide an efficient and often specific water flow and enable them to transport water into and out of the cells along the water potential gradient.
B Without energy cells would be forced to enter into a state of dormancy. C Energy is required to process genetic information–without an active DNA molecule cells will be unable to function. D Energy is required in order to maintain homeostasis–without a constant organized internal state the cell will die.
Membrane Structure and Function net water movement into cell Osmosis and Living Cells. Outside of cell has same solute as inside of cell Hypertonic Solution. Outside of cell has higher solute than inside of cell Hypotonic Solution.
Inside of cell has higher solute than outside of cell Tonicity. In order for cells to survive they require nutrients in the form of glucose and minerals plus oxygen. Additionally they need to dispose of waste products.
Cells also rely on their organelles and diffusion for survival. Without oxygen minerals and the removal of waste products cells do not survive. In animals blood delivers the necessary.
Three additional aquaporins are present in the kidney. AQP6 is present in intracellular vesicles in collecting duct intercalated cells and AQP8 is present intracellularly at low abundance in proximal tubules and collecting duct principal cells but the physiological function of these two channels remains undefined. Cells there is a greater control of water flow through the membrane causing a faster or slower flow rate.
The faster flow occurs through proteins called aquaporins Agre and Kozono 2003 which are characterized in the next section. AQUAPORINS Aquaporins also known as AQPs were first reported in 1988 by Denker et al who. For any living organism integral membrane proteins constitute around 30 of the proteome 1This large number reflects that a fundamental requirement for life is the capacity of each living cell to.