No if you can reconstitute an aquaporin in a membrane it will function fine. What is the role of aquaporins in the kidney.
Do aquaporins require a living cell in order to function.
Do aquaporins require a living cell to function. Yes all living things are made up of cells. No if you can reconstitute an aquaporin in a membrane it will function fine. Aquaporins that actively transport water will not function but many aquaporins are passive transporters.
All the above being said we are still not close enough to use aquaporins as well as biology does. Do Aquaporins Require A Living Cell To Function. Do Aquaporins Need Living Cells to Work.
Aquaporins are just water channels that allow water molecules to pass through the membrane. They were kept in mind and work is still going on. Do aquaporins require a living cell in order to function.
No if you can reconstitute an aquaporin in a membrane it will function fine. Aquaporins that actively transport water will not function but many aquaporins are passive transporters. Do aquaporins require a living cell in order to function.
No because its just a channel for water to pass through it doesnt need a living cell to facilitate it. It also says that Agre also ran the experiment with artificial cells and it still worked. Functions for some aquaporins have also been suggested such as cellcell adhesion membrane polarization and regulation of interacting proteins such as ion channels.
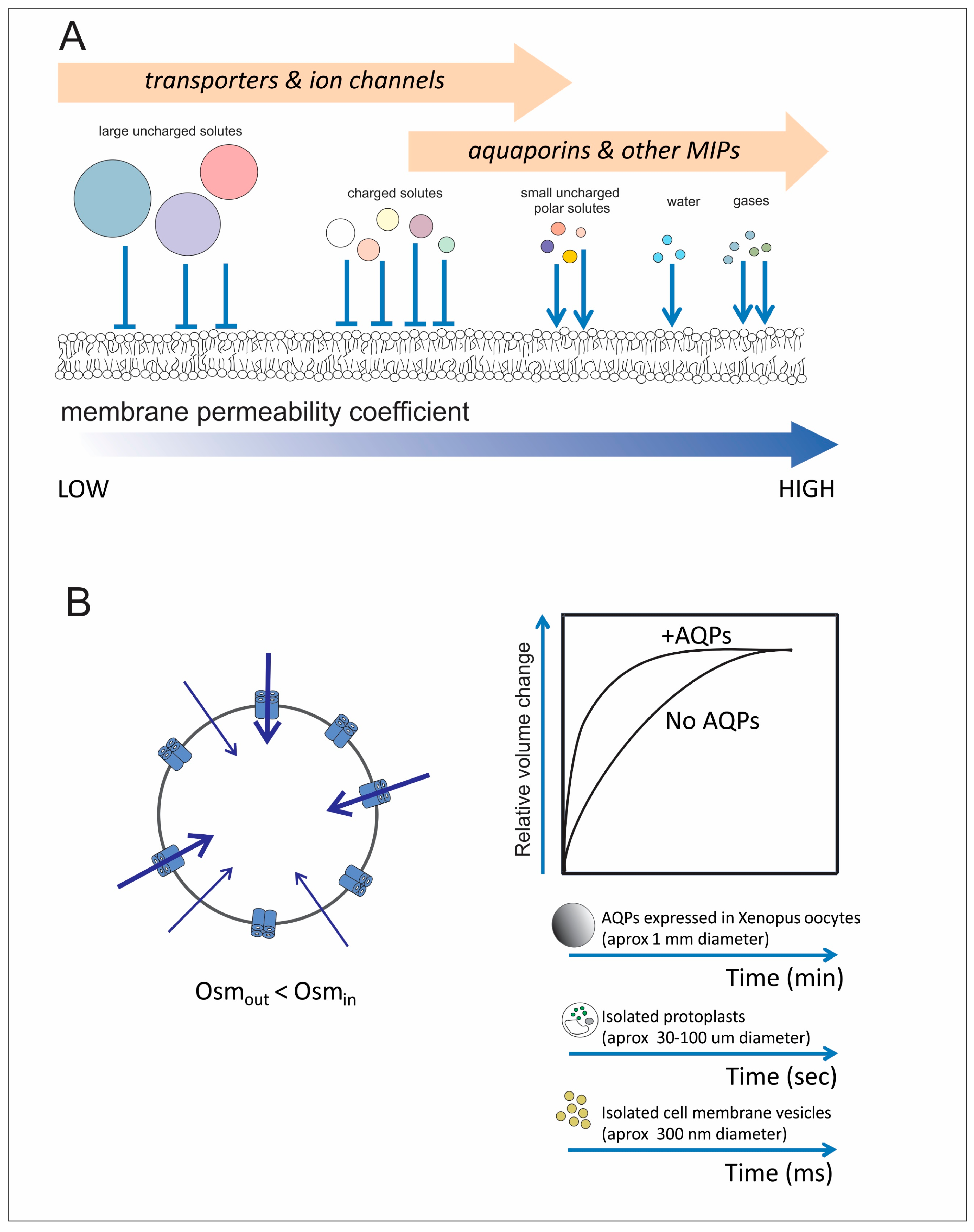
Why do some membranes need high water or glycerol permeability. Most cells do not express aquaporins. Virtually all biological membranes are reasonably water permeable as.
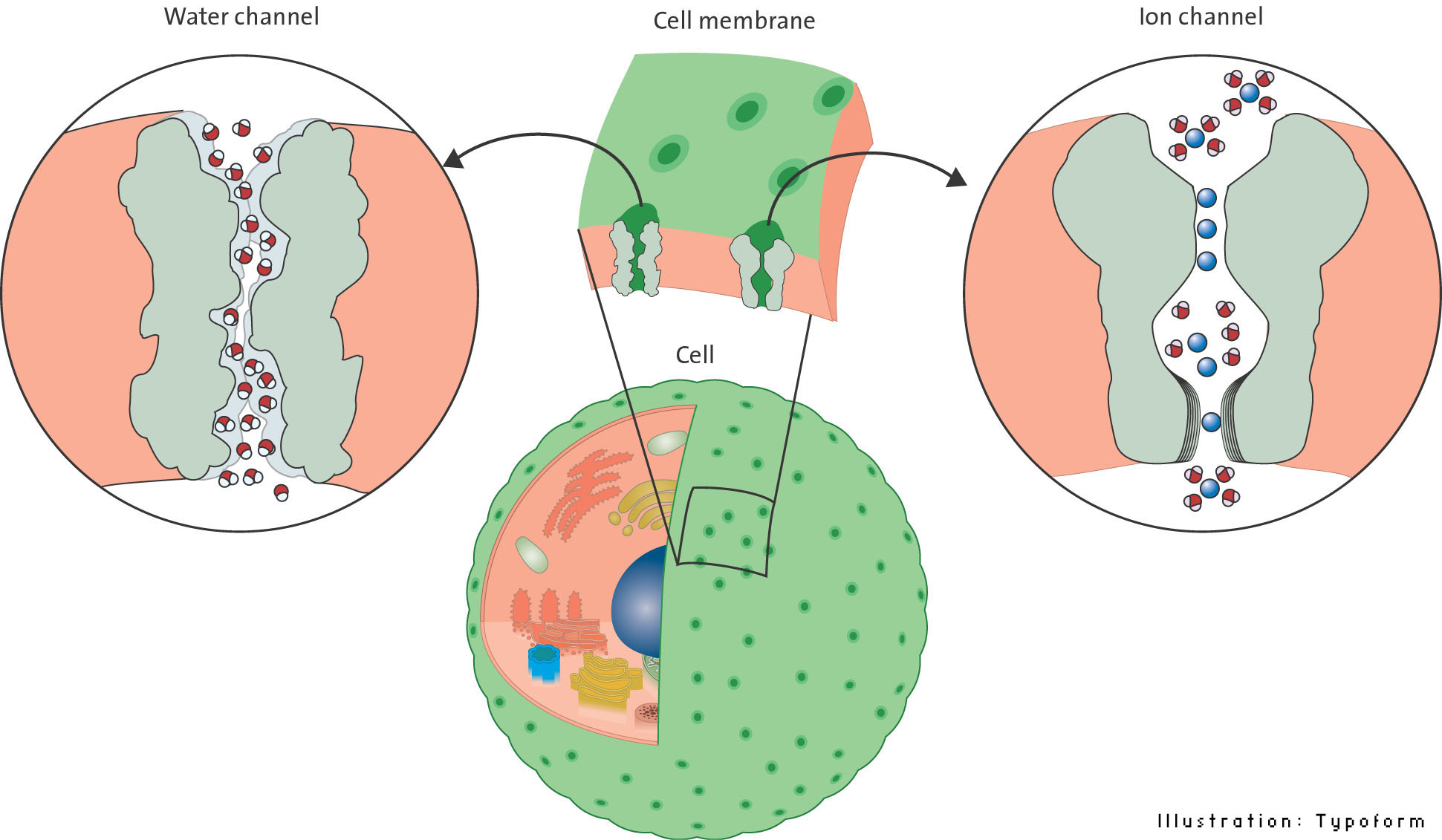
- Aquaporins do not require a living cell in order to function because it is a mere channel for water to pass through. How does the aquaporin prevent H ions from passing through. - Aquaporins prevent H ions from passing through because they are selective and anything that is polar like these hydrogen ions will be rejected due to their charge.
What is the role of aquaporins in the kidney. How did Agre use a simple osmosis experiment to prove the function of aquaporins. Do aquaporins require a living cell in order to function.
How does the aquaporin prevent H ions from passing through. What is the role of the aquaporins in the kidney. Aquaporins regulate the water flux in the kidney and prevents the bursting of cells.
The primary function of most aquaporins is to transport water across cell membranes in response to osmotic gradients created by active solute transport. Because the water transport capacity of aquaporin monomers is low membranes often contain a high density of aquaporins up to 10000 per square micron to increase water permeability substantially above that in the absence of aquaporins. It is important to remember that aquaporins do not actively transport water across the cell membrane.
Instead they facilitate the diffusion of water across the cell membrane. Due to the slow diffusion of water across the lipid bilayer aquaporins effectively increase the. The human body consists of 70 water contained in every cell.
It is vital to life that this perfect cellular water balance be constantly maintained for the body to function as it should. This is where Aquaporins and their importance to water and to life come into play. Aquaporins also called water channels are channel proteins from a larger family of major intrinsic proteins that form pores in the membrane of biological cells mainly facilitating transport of water between cells.
The cell membranes of a variety of different bacteria fungi animal and plant cells contain aquaporins through which water can flow more rapidly into and out of the cell than by diffusing. The cell membrane makes the cell a compartment separate from the extracellular environment. What is the other main function of the cell membrane.
A Compartmentalizing organelles within the cell. B Facilitating the migration of the cell through the body. As aquaporins are essential to life it is only to be expected that dysfunction of these membrane proteins may cause or contribute to disease.
Aquaporins have been associated with critical water transport in the kidneys lungs and skeletal muscle. Further aquaporins are part of the blood-brain barrier. Aquaporins are membrane water channels that play critical roles in controlling the water contents of cells.
These channels are widely distributed in all kingdoms of life including bacteria plants and mammals. More than ten different aquaporins have been found in human body and several diseases such as congenital cataracts and nephrogenic. Water crosses cell membranes by two routes.
By diffusion through the lipid bilayer and through water channels called aquaporins. Functional characterization of the first aquaporin was reported in 1992 but water channels were suspected to exist well before that time because the osmotic permeability of some types of epithelial cells was much too large to be accounted for by simple diffusion through the. Aquaporins belong to the group of integral membrane proteins that are found in cell membranes.
The role of aquaporins is to allow the passage of water between cells. Most cell membranes have many aquaporins so the cell can react quickly to consistently maintain proper balance within the cell. Osmoregulation is important to all cells.
Aquaporins and the relations between environmental factors and plant aquaporins. Complete understanding of aquaporin function and regulation is to integrate those mechanisms in time and space and to well regulate the permeation of water across biological membranes under changing. If aquaporins allowed ions through their channels all ion concentration gradients across the cell membrane would approach zero ie all ions would be in equilibrium and the cell would not be able to perform many of its critical functions that depend on the concentration gradient of various molecules eg many.
Aquaporins are expressed in organ- tissue- and cell type-specific manners. Knowledge of the expression patterns of different aquaporins is essential for several reasons. Firstly it will provide clues to the function of aquaporins at the whole plant level.
Plant aquaporins exhibit a remarkable multiplicity of isoforms. Genome sequencing has established the exact number of aquaporin genes to 35 in Arabidopsis and 33 in rice In addition expressed sequence tags corresponding to 36 aquaporin isoforms have been identified in maize Based on sequence homology plant aquaporins can be subdivided in four subgroups which to some extent. This has the effect of concentrating the solutes left in the cell making the cytosol denser and interfering with diffusion within the cell.
The cells ability to function will be compromised and may also result in the death of the cell. Various living things have ways of controlling the effects of osmosisa mechanism called osmoregulation.